UltraVnc Nat 2 Nat Connections
Description
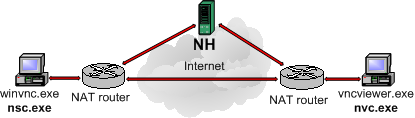
Network Address Translation (NAT) is a method of connecting multiple computers to the Internet (or any other IP network) using one IP address. This allows home users and small businesses to connect their network to the Internet cheaply and efficiently. For a detailed description of NAT see e.g. here. UltraVNC provides a connection method for UltraVNC server and viewer which are located behind (different) NAT routers. This can be used without any router modification.
How does it work
The connection is established with a helper service (NH, i.e. NAT helper) located in the Internet. The helper service only aids during initiation of the connection, the actual VNC connection goes directly from NSC to NVC (NAT Server Connector and NAT Viewer Connector).
Below is a diagram with the steps necessary to establish a connection. First both the viewer and the server side contact the NAT helper (NH). The NAT helper then provide both sides with the necessary information to make a direct connection.
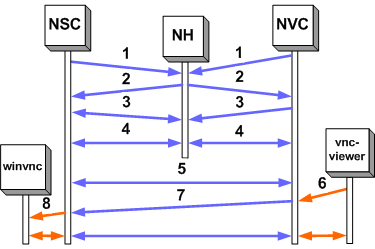
- Member
- Challenge
- Encryption
- Keep alive NxC to NH
- Keep alive NSC to NVC
- Viewer connect
- Data NSC/NVC
- Connection to winvnc server
Steps 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 7 are UDP, steps 6 and 8 are TCP.
Run nsc.exe (on PC running winvnc.exe, normal mode)
Run nvc.exe (on the PC you want to start to viewer)
Double click nsc.exe icon, then enter member name and
passwd.
Double click nvs.exe icon, then enter same member name and
passwd
The systray icon indicates the connection status:
![]() not connected
not connected
![]() NH server found and connected (step 4)
NH server found and connected (step 4)
![]() NSC and NVS are directly connected (step 7)
NSC and NVS are directly connected (step 7)
On green icon you can start vncviewer.exe: connection localhost, default port (5900)
Sometime it can take some time and 2 or 3 cycles before icons become green (1-5 minutes). This happens especially when you are using a dynamic/ip for the NAT router.
Currently a little debug window is open during steps 1 to 5.